Crypto is reshaping our financial systems. It differs from traditional money in many ways, yet brings lots of benefits to those in the loop. But if you haven’t dealt with it yet, where do you start, and what should you know? On this page, we’ll go over the crypto basics, including what is cryptocurrency and how it works.
Key takeaways:
- According to the definition of crypto, it is a kind of virtual currency that isn’t controlled by a central authority like a government.
- Its fundamental parts are decentralization (distributed ledger technology), cryptography, and blockchain.
- The main types of crypto include native coins, tokens, stablecoins, and NFTs.
- Crypto can be used for investment purposes, for making online payments and cross-border transfers, as well as for iGaming, gambling, logistics management, and other reasons.
What Is Cryptocurrency?
The term cryptocurrency (other names are “crypto currency” or “crypto”) refers to virtual currency, or rather, decentralized digital money. It exists online and isn’t backed by physical bills or coins.
What does cryptocurrency mean if we compare it with government-issued fiat currencies like US dollars? Unlike them, crypto is intended to be used as a medium of exchange over a computer network. That is, they operate on decentralized blockchain networks, which are distributed ledgers that are maintained by a network of computers, often referred to as nodes.
This kind of approach makes peer-to-peer transactions possible, omitting the necessity to rely on intermediaries like a traditional banking system. Such financial transactions typically cost less and are faster than using regular banks, especially when making global cross-border transfers. Cryptocurrency has become an independent asset class in the modern financial world and is constantly growing and developing into various forms of use.
When and how did cryptocurrency start? And why was cryptocurrency created? Crypto emerged back in 2009 when Satoshi Nakamoto introduced Bitcoin (BTC) in an attempt to establish a decentralized financial system at a perfect time right around the global financial crisis of 2008. Bitcoin’s pioneering blockchain technology paved the way for the emergence of other cryptos during the next decade together with smart contracts and other tech innovations in the industry.
Key Characteristics of the Cryptocurrency

To better understand what’s cryptocurrency all about, let’s overview some of the core features that distinguish it from traditional money.
Decentralization
What is the purpose of cryptocurrency? The answer lies in the classic crypto definition that features decentralization. This implies that the blockchain and currency aren’t regulated by any single financial institution, central bank, or government. Therefore, it’s not as susceptible to control by central authorities and censorship, so there’s a smaller chance of your assets getting frozen or other manipulations occurring.
Security
Cryptocurrencies are decentralized in distributed network nodes that verify transactions using cryptographic algorithms, which protect data. The transactions are then recorded in the blockchain, a publicly available distributed registry. Each transaction is distributed over a peer-to-peer network scattered all over the world and is replicated by many nodes within a few seconds. Only public and private keys confirm ownership and give access to the assets.
Higher Anonymity
One of the most notable cryptocurrency advantages is that not all transactions have to be directly linked to personal information or the real identity of a user, offering some privacy and anonymity. Depending on which exchange or payment method is used, users sometimes do not identify themselves when making transactions with cryptocurrency, as at times minimum verification and a wallet address are enough. After verification, the decentralized network confirms the transaction and writes it into the blockchain in the required form.
Some cryptocurrencies (for example, Bitcoin) use a system of private and public keys to carry out the necessary authentication of these transactions. Thus, users have the opportunity to create anonymous digital identity cards and digital wallets. This helps them not only to make transactions in a decentralized system but also to authenticate them securely.
Immutability
The irreversibility and immutability of cryptocurrency are demonstrated by the fact that only the owners of the corresponding private keys have the opportunity to move their digital assets. If a transaction has already been recorded in the blockchain, it can no longer be changed or deleted. This makes the records tamper-proof.
Scarcity
The supply of most cryptocurrencies is pre-determined and encoded into the algorithm used to create them. For example, there is a maximum supply of Bitcoin. Once the limit of 21 million Bitcoins is reached, no one will be able to mine any more of this coin. A deliberate scarcity and capped supply of cryptocurrency prevents currency manipulation, places constraints on inflation, and resists a decrease in value over time.
Volatility
Who controls the value of cryptocurrency? Although some currencies are backed by stable assets like fiat currency, most cryptocurrency prices could get shaky. A mix of factors can make the prices for crypto unstable, including demand and supply fluctuations, market speculation, external events, regulatory changes, among other price swing causes.
So although crypto presents great investment opportunities, it could be risky on the flipside. For example, the value of game tokens is directly affected by the size of their player bases, and if the game loses popularity, their value automatically goes down too. Not to mention that the reward pool might decline as well, restricting earned payouts.
What Is Cryptocurrency Used For?
Crypto is a lot more than just a medium of exchange. They’re applied in lots of industries and for various use cases, here are several examples.
- Non-commercial money transfers — international transfers and cross-border remittances are rather quick and low-cost, allowing people to bypass traditional banks and traditional payment processors.
- As a payment method — a growing number of e-commerce stores and online retailers like Microsoft, Home Depot, and other companies are expanding their boundaries by accepting certain cryptocurrencies for their goods.
- Trading and investment — some people see crypto as an investment opportunity and trade currencies to make a profit off the exchange rate differences or earn interest by storing crypto assets on select exchanges that offer staking opportunities.
- Lending and decentralized apps — some platforms and applications like Solana and Ethereum let people use smart contracts to lend money to each other and use decentralized exchanges (DEXs) and NFT marketplaces.
- Logistics — blockchain technology is also applied in supply chain management, helping people track goods, trace their journey, and minimize fraud.
- Charity — lots of non-profit organizations accept crypto for donations, so people can contribute to meaningful causes, tracking exactly what these funds were spent on.
- Gambling and betting — many people place bets or gamble in crypto casinos like BitStarz or FortuneJack due to their anonymity, availability in regions where regular casinos are off-limits, and their support of different kinds of crypto, simplifying deposits and withdrawals.
- iGaming — lots of online games support crypto like Bitcoin, Ethereum, or Litecoin allowing users to buy items and earn rewards. Some blockchain-based games even have their own tokens and cryptocurrencies such as Decentraland (MANA), The Sandbox (SAND), or Axie Infinity (AXS), certain assets may be converted to other cryptocurrencies or fiat money while others like BombCrypto (BCOIN) typically have little utility outside their ecosystem.
How Does Cryptocurrency Work?
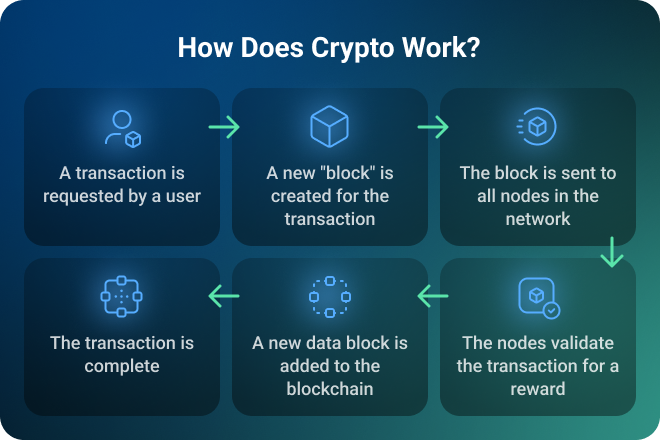
Essentially, crypto is just a new way to handle money without middlemen. Let’s dissect three basic terms — decentralization, blockchain, and cryptography, to get to grips with how cryptocurrency works.
Decentralization in the blockchain is the main distinguishing feature of cryptocurrency and one of the key factors behind its successful application. It distributes information across many network participants, so the ledger is public and no individual is in single control. Plus, it’s transparent which raises trust.
What is a blockchain in crypto? The definition of cryptocurrency won’t be complete without mentioning the blockchain, which is a distributed database that keeps track of how many assets certain users have, including balances and transaction histories. This database is divided among its users and shared across a broad network made up of thousands of nodes or computers that serve to secure and decentralize the recording of transactions.
Importantly, all transactions are permanently added to the blockchain and are immutable. They are unchangeable, so you can’t erase or modify them, which provides high security.
Now let’s explain cryptocurrency operation peculiarities. Cryptography is like a secret code for securing transactions. This mathematical and computational practice is applied to encode and decode data, it ensures the security necessary for conducting transactions on the network.
Specifically, every transaction is put in a block that’s validated by participants of the network who confirm legitimacy and add it to the chain. They use consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work or Proof of Stake to ensure no one cheats or tries to double-spend. Also, it is impossible to control the generation of new monetary units without it.
To keep the assets safe, a user gets a set of keys: a public key that’s like an account number you can share with others. A private key is a password to prove your ownership, access crypto assets, and sign off transactions.
A few other things you should know about how crypto works is that there are multiple ways to buy crypto. For instance, you can purchase it with fiat money like euros or dollars, trade it for other crypto on exchanges or other platforms, or earn it in games or online casinos. Once you have some, it goes into a crypto wallet that keeps your keys. You may store the assets as an investment or transfer them if you want to pay for something.
Types of Cryptocurrencies
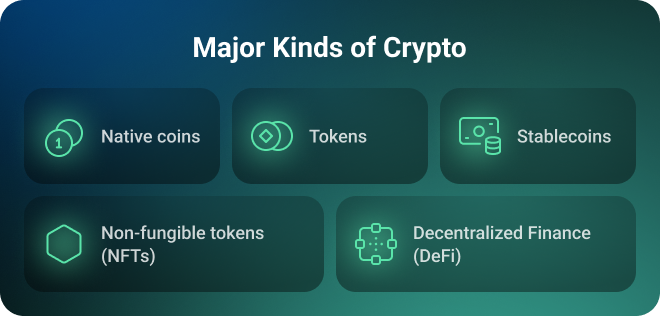
What are cryptocurrencies, and how do they differ from coins and tokens? There is a difference between the terms, their purposes, use cases, and technologies. For starters, any cryptocurrencies apart from Bitcoin are called alternative coins. Let’s dot the i’s by overviewing several categories.
Native coins — like Bitcoin (BTC), Ethereum (ETH), Litecoin (LTC), or Solana (SOL) aren’t the same thing as tokens as they operate on their own blockchains and are typically designed as an exchange medium.
Tokens — do not have their own blockchains but perform the function of digital assets, they are built on top of an existing blockchain platform for a certain cause. For instance, there are utility tokens for a specific ecosystem like the Basic Attention Token (BAT), decentralized exchange tokens like Uniswap (UNI), or security tokens like tZero representing someone’s ownership of assets such as real estate.
Stablecoins — such currencies as Tether (USDT) or USD Coin (USDC) rely on existing blockchains but are backed by commodities or stable assets like gold or fiat money. This means that, unlike other cryptocurrencies whose prices can change throughout the day, their prices are linked to tangible assets to minimize their price volatility and reduce risks.
Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) — NFTs like CryptoPunks are very popular among collectors and are used to represent a person’s ownership of items like art objects, assets in a game, or even music, they can’t be split into smaller units or swapped for other tokens.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) — is not a separate type of cryptocurrency but a comprehensive platform for lending, trading, and other purposes. It can combine different types of digital assets, however, users can, for example, use Compound (COMP) or Aave (AAVE), to pay for services directly or receive funds without the need for intermediaries.
What Is Crypto Money? Pros and Cons of Different Types of Cryptocurrency

No two types of cryptocurrencies are identical. They all differ from each other in some characteristics: transaction speed, reliability, transparency, history, and many other qualities. These are some of the pros and cons of the most popular cryptos.
Bitcoin (BTC)
Pros:
- Accessibility for everyone, even if they don’t have a bank account.
- Sending payments is as simple as possible, instant payments worldwide to anyone.
- Freedom from any political influence, no governments or banks control it.
- Due to the fact that wallet addresses are secret, Bitcoin payments are private.
- Payments are irreversible and immutable.
- Bitcoin is secured by a decentralized blockchain that cannot be hacked or modified.
Cons:
- Lack of government protection, unlike using a traditional bank account.
- Bitcoin’s price volatility continues to be observed despite the long-term growth in the value of assets.
- The irreversibility of payments is not always positive. After making a payment, you will not be able to cancel it.
Bitcoin Cash (BCH)
Pros:
- Increased cryptocurrency block size. Since 2018, the Bitcoin Cash block size has been increased from 8 MB to 32 MB which made it possible for the network to process up to 40,000 transactions per second. The large block size helps to reduce the cost of transactions.
- Bitcoin Cash has the ability to accept transactions without the usual confirmation in its blockchain. Therefore, this network provides miners with special tools — these are identifiers for tracking coins. This additional protection eliminates the risk of coins being used multiple times.
- In order to expand the possibilities of cryptocurrency, the developers of the Bitcoin Cash platform are implementing smart contracts.
Cons:
- Initially, disputes in the community arose due to changes in the protocol and the way the cryptocurrency was developed. Because of these disagreements, factions within the community have arisen, and there have been hard forks (Bitcoin Cash ABC and Bitcoin Cash SV). This hinders the stability and predictability of the project.
- Bitcoin Cash (BCH) does not have the same prevalence as Bitcoin as a means of payment. Such a low degree of acceptance makes the use of BCH in everyday transactions more limited.
Litecoin (LTC)
Pros:
- Open-source code that allows you to quickly make changes to the protocol.
- Flexibility in adding technological innovations that increase the convenience and speed of transactions (Lightning Network protocol, SegWit).
- The transaction speed is 2.5 minutes.
- Simultaneous processing of up to 56 transactions at a time.
- The presence of an upper limit on the number of coins (84 million coins).
- A simple mining process.
- Convenience for trading and exchange as most platforms and wallets support Litecoin.
Cons:
- Surpassing Bitcoin in many characteristics, Litecoin is portrayed as similar to Bitcoin. After Bitcoin adopted the SegWit protocol, Litecoin lost something that made it unique in terms of unique branding.
- Lost trust occurred after Charlie Lee sold his assets in LTC in 2017. The Litpay service stopped functioning, and this negatively affected the market.
- The image of LTC is regularly harmed by the fact that it’s used by around 30% of underground sellers.
Ethereum (ETH)
Pros:
- Strong core development team.
- The dynamic dApps ecosystem and various blockchain-based projects are constantly evolving and improving within the community of developers, investors, and users.
- Potential for high returns, and the more widespread the platform becomes, the higher the prices of Ethereum rise.
- Ethereum has many use cases from decentralized finance (DeFi) to interchangeable tokens (NFT). Accordingly, there are also more ways to invest in Ethereum.
- Convenience in buying and selling for investors with any level of training.
Cons:
- High volatility and constant price fluctuations can be associated with significant losses for investors.
- The lack of regulation increases the risks associated with investing in Ethereum.
- There is growing competition from other platforms to create decentralized applications (for example, Cardano and Polkadot).
Ethereum Classic (ETC)
Pros:
- High immutability as the active team of miners of this cryptocurrency does not allow it to be branched.
- Neither third parties nor intermediaries have the right to participate in peer-to-peer purchases/sales or exchanges. Transactions are also free from the control of restrictive governments. Moreover, Ethereum Classic supports decentralized applications and smart contracts.
- The price of the ETC token is lower than that of ETH so it may be attractive for novice investors.
Cons:
- Lack of backward compatibility with Ethereum.
- The Ethereum Classic platform is almost entirely owned by Parity Technologies which raises investors’ concerns about whether ETC will remain decentralized.
- The ETC token does not have sufficient protection against 51% of attacks. This casts doubt on the image of Ethereum Classic.
Ripple (XRP)
Pros:
- Transactions conducted using XRP are known for their lightning speed (up to 1,500 transactions per second). This attracts those who need to make fast cross-border payments.
- Strong partnerships with major financial institutions around the world. For this reason, XRP was legalized and distributed in the financial sector.
- XRP differs from many other cryptocurrencies in that it has regulatory clarity from the authorities in some countries. This provides investors with confidence in the long-term viability and reliability of XRP.
Cons:
- XRP is controlled by Ripple. This gives rise to concerns about centralization and control.
- The U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has raised some questions with Ripple in connection with the sale of XRP. In this regard, some investors avoided this cryptocurrency. Legal issues have created uncertainty about the future of XRP.
Tether (USDT)
Pros:
- This stablecoin has high liquidity compared to other digital assets. It can easily be exchanged for fiat currency.
- It’s an attractive means for making payments due to low volatility.
- Numerous cryptocurrency exchanges and platforms support Tether. Its widespread recognition makes it convenient to buy, sell, and exchange for other digital assets.
Cons:
- There is no evidence of full provision of fiat reserves which raises doubts about the legitimacy of the token as a stablecoin.
- Earlier, the parent company of Tether, iFinex, was fined for non-compliance with the rules by the Attorney General of the state of New York. Now, Tether is suspected of acting on the same principle as its parent company. This harms the image of the platform and the credibility of the stablecoin.
Axie Infinity (AXS)
Pros:
- Two tokens are in use Axie Infinity Shards (AXS) and Smooth Love Potion (SLP) for governance and allowing users to gain rewards for gameplay like battling creatures called Axies.
- Players have the chance to earn by participating in the games.
- Ecosystem participants have a voice in many game development decisions.
Cons:
- Getting your first tokens can be costly, making the entry barrier quite expensive for newbies.
- Sustainability and volatility are big concerns as user growth is integral for the ecosystem to grow and be stable.
Decentraland (MANA)
Pros:
- Users govern the platform, enhancing transparency and boosting community decision-making.
- Allows users to buy virtual plots of land in this metaverse and monetize it.
- People are free to create their own apps, experiences, and games, resulting in an array of use cases from art galleries to various virtual events.
Cons:
- Decantraland’s MANA has limited value beyond the platform.
- Price fluctuations are possible.
- Other emerging platform analogs can outcompete it, diluting the value of investment in Decentraland.
Buying and Storing Cryptocurrency

One more key to understanding cryptocurrency is figuring out how to purchase and keep it.
A person can get crypto in various places, but the most widespread starting point for cryptocurrency trading takes place on special platforms known as — cryptocurrency exchanges. Centralized ones like Kraken, Coinbase, or Binance typically have relatively low commissions and their interfaces are user-friendly and suitable for newbies. Lots of different currencies and trading pairs are available, prices for crypto are rather stable, and it’s generally possible to purchase crypto with fiat money. However, there’s a detailed Know Your Customer identity verification procedure.
Those who value anonymity or seek unique tokens or coins often go to decentralized exchanges like Uniswap. However, new crypto investors may be intimidated by the complex interfaces created for different types of transactions. Extended performance charts and other features can also be difficult to grasp.
How else can you buy cryptocurrencies? For instance, in physical machines called crypto ATMs, on P2P marketplaces like Paxful, or through a cryptocurrency broker like Robinhood. Brokers help to make the process of buying cryptocurrencies as simple as possible, but they may charge a high commission.
What happens after you buy crypto? Well, you will immediately have to consider where to store the assets you purchased. The main thing that you should know is that you cannot keep crypto in your traditional bank account.
As such, if you’re buying crypto on a centralized exchange like Kraken, you’ll have the chance to leave your assets in the exchange’s on-platform wallet. Although it’s convenient for frequent trading and you can be offered to earn on staking, this isn’t the safest option, as exchanges may be hacked.
There are special hot and cold wallets for storing cryptocurrencies. Hot wallets are standalone digital storage solutions like MetaMask, while cold wallets could be something as simple as a private key written on a piece of paper or a secure device solution like Ledger Nano. There are more storage options out there, your task is to choose a reliable, safe, and affordable option suitable for your needs.
Taxation and Legal Status of Cryptocurrencies
The jurisdiction regarding crypto also differs from country to country. In some locations like China using crypto is banned, and it’s illegal to use it for payments or other activities together with traditional currencies. Others allow limited use for certain cases. Specifically, the USA, Canada, most European Countries, and Japan pose strict regulations.
Cryptocurrency trading is often taxed in different countries, for instance, in the US it’s regulated by the IRS and has anti-money laundering (AML) laws. This means that if a user receives crypto as payment for goods or services, there will likely be an income tax on the profit. The specific rates to calculate the tax vary. As such, India charges a 30% flat tax on gains.
Plus, some jurisdictions even impose taxes on trading, and since cryptocurrency exchanges often cooperate with tax authorities, evasion is not only fraught with large fines but also very difficult. That’s why it is important to keep track of the transactions, recording data like amounts, dates, and the market values of traded assets. Based on this, be sure to discuss your liabilities with a tax consultant.
Are there cases when crypto isn’t taxed? It depends on the person’s location, asset sizes, and other factors. But generally, if you purchase crypto using fiat money, make microtransactions that don’t exceed a certain threshold, or donate crypto to specific charities, this usually isn’t taxed.
The Present and Future of Cryptocurrency
Today, cryptocurrencies are already an integral part of the financial world. The rapid development of blockchain technology and the growing popularity of digital assets are increasingly affecting the modern world. There are many challenges and opportunities ahead. Among the expected forecasts, the following can be distinguished.
Popularization and Mass Acceptance
Many large corporations, such as Tesla and PayPal, already accept some digital assets as payment. More and more people are starting to use cryptocurrency for various purposes. Therefore, there are signs that cryptocurrencies will become a full-fledged part of the global economy.
Changes in the Regulation and Legal Status
The more digital assets are developed, the more attention governments around the world are paying to the sector. Their main task is to create a legal framework for protecting investors and countering financial crimes. Moreover, some are looking into the opportunities of governmentally-backed Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs), which may emerge soon.
Possible Danger
And yet, the existence of cryptocurrencies is not considered an unambiguously positive fact in all countries. There is a possibility that they will be banned in some jurisdictions. In addition, the danger of major cyber-attacks, as well as data leaks, is always present. They can cause a big blow to the crypto industry and raise investor distrust.
Concluding Thoughts on What Is Crypto
Hopefully, now you know the answers to questions like “What is cryptocurrency and how does it work?”. The number of various kinds of currencies, tokens, and coins continues to grow. The same applies to their use cases, from charitable activities and trading to gaming, logistics, and beyond. In the following chapters, we’ll dive deeper into the peculiarities of purchasing and storing crypto safely.